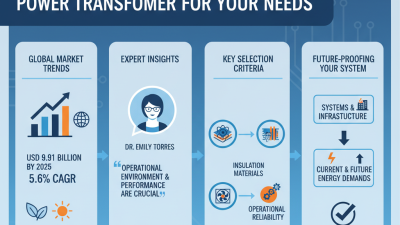
Improving electrical transformer efficiency is crucial for optimizing energy use. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in the field, "Higher efficiency in transformers directly reduces energy waste." This quote underscores the importance of focusing on transformer design and maintenance.
Transformers play a vital role in power distribution. The efficiency of these devices impacts energy costs and environmental sustainability. For instance, a slight increase in efficiency can lead to significant savings over time. However, many transformers operate below their optimal performance levels. Regular assessments and upgrades are often neglected, leading to inefficiencies.
Investing in advanced materials and technology can enhance electrical transformer efficiency. Yet, some organizations resist change due to costs or lack of awareness. This reluctance can hinder progress and lead to wasted resources. Embracing innovation in transformer technologies is necessary for a more efficient energy future.
Electrical transformers play a crucial role in power distribution. Their efficiency significantly impacts energy consumption and operational costs. Recent studies indicate that typical transformer efficiency ranges from 95% to 99%. This means that 1% to 5% of energy is lost as heat. Improving this efficiency is essential, especially as energy demands rise globally.
Understanding transformer efficiency is vital. A 2019 report by the International Energy Agency highlighted that transformer losses account for approximately 8% of total energy losses in electrical systems. These losses could lead to substantial economic costs, estimated at billions of dollars annually. Furthermore, inefficient transformers can cause unwanted heat generation, affecting surrounding equipment. This situation creates an urgent need for better monitoring and maintenance practices.
Companies should adopt advanced technologies. Using smart sensors can help track performance and identify inefficiencies. Additionally, upgrading to higher-quality materials can reduce losses. Though many transformers are built with standard materials, investing more upfront can yield long-term energy savings. Ignoring these aspects may lead to the deterioration of overall system performance over time. Addressing inefficiencies is a responsibility that needs attention.
| Parameter | Value | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Load Factor | 0.8 | Higher efficiency at rated load. |
| Cooling Method | Oil-immersed | Improves heat dissipation and overall efficiency. |
| Winding Material | Copper | Better conductivity leads to lower losses. |
| Core Material | Silicon Steel | Reduces hysteresis losses, increasing efficiency. |
| Transformer Age | 10 years | Regular maintenance needed to maintain efficiency. |
| Efficiency Rating | 98% | High efficiency reduces operational costs. |

Transformer efficiency is crucial for effective energy distribution. Several factors influence how well a transformer performs. One significant aspect is the core material. Amorphous steel cores can reduce losses by up to 30% compared to traditional silicon steel. This change can lead to better energy conservation.
Losses due to heat can also affect performance. Heat dissipation during operation affects overall efficiency. According to a report from the International Energy Agency, reducing heat losses can greatly enhance performance. Proper insulation and cooling systems play a critical role.
**Tips:** Regular maintenance is essential. Check for overheating signs. Replace old components proactively. Optimizing load can also help. Running transformers at near-rated loads can decrease losses. Awareness of efficiency can lead to better performance.
Design flaws can impair efficiency. Not all transformers are made equally. Some may have poor winding designs, resulting in higher losses. It's important to evaluate design choices critically. Even small adjustments can yield significant improvements in transformer performance.
Reducing core losses in transformers is essential for enhancing efficiency. Core losses primarily arise from hysteresis and eddy currents in the transformer core. According to industry studies, core losses can account for up to 95% of the total losses in a transformer. Utilizing high-quality silicon steel can significantly reduce hysteresis losses. This material has higher magnetic permeability, leading to improved efficiency.
Another effective technique is to optimize the core design. The shape of the core influences magnetic flux distribution. For instance, the toroidal transformer design minimizes losses compared to traditional designs. Reports indicate that toroidal transformers can reduce core losses by approximately 30%. However, not all applications can accommodate such designs due to space constraints or specific performance requirements.
Properly sizing the transformer can also mitigate core losses. An oversized transformer may operate inefficiently at low loads, increasing loss percentages. Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial. They help identify potential issues that can exacerbate core losses. Careful attention to these factors ensures better transformer performance, but achieving optimal efficiency remains a challenge. Continuous improvement efforts are necessary.
To enhance the efficiency of electrical transformers, focusing on winding design and materials is crucial. Winding losses, which account for a significant portion of transformer inefficiency, can be reduced through refined designs. Utilizing larger conductors can lower resistance, yet this may increase material costs. Striking a balance between cost and efficiency is essential. Recent studies indicate that optimizing the winding geometry could yield efficiency improvements of up to 5%.
Material choice also significantly impacts transformer performance. High-conductivity copper is widely used, but aluminum presents a lighter, often less expensive alternative. A report by the International Electrotechnical Commission suggests that using superconducting materials could improve efficiencies by over 10%. However, these materials are not always practical due to their cost and operational challenges.
The insulation system is another area of concern. Traditional insulation materials often have thermal limitations, which can lead to overheating and losses. Newer, high-performance insulating materials can withstand higher temperatures and reduce losses, yet they could complicate manufacturing processes. Reflecting on these trade-offs is vital for engineers seeking better designs. Efficiency gains are possible, but they require careful consideration of materials, design, and overall system impact.
Maintaining electrical transformers is crucial. Regular maintenance practices can enhance efficiency and performance. According to industry reports, up to 30% of transformer failures arise from poor maintenance. Hence, implementing a robust maintenance strategy becomes essential.
One key practice is thermal imaging. This method can identify hot spots caused by loose connections or overload. By detecting these issues early, operators can avoid catastrophic failures. Another vital maintenance task is checking fluid levels. Proper insulation fluid is necessary to keep transformers cool. Neglecting this can lead to overheating, resulting in reduced efficiency.
Documentation is often overlooked. Keeping accurate records helps understand performance trends. These details can guide future maintenance decisions. Regular inspections, ideally every six months, play a significant role. Timely interventions can prevent unexpected downtimes and prolong transformer life. Ignoring maintenance can lead to significant losses, both financially and operationally. A proactive approach is the best strategy.